3D-4D Sonography
What is 3D-4D Sonography?
Ultrasound scans/sonography works on the principle of sound reflection. It generates high-frequency sound waves to create images in 2D, 3D and 4D. The images can be viewed as pictures on a video screen/monitor.
The standard 2D ultrasound, more commonly used in routine ultrasound of body parts, other than gynec and obstetric purposes, shows a black and white picture on a screen.
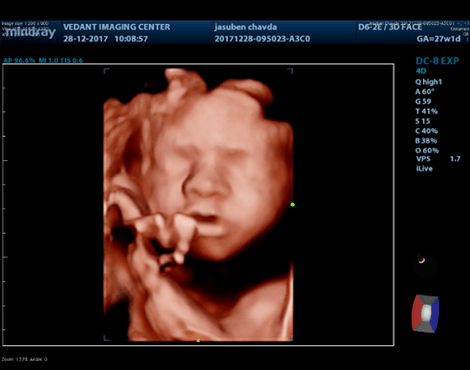
3D and 4D ultrasounds are widely used in obstetric practice. A 3D ultrasound creates a different perspective by merging a series of 2D images taken from various angles into a composite to form a 3D picture.
4D ultrasound is different from a 3D ultrasound because it adds the dimension of time, providing a live video of the baby in action: kicking, stretching, yawning and sucking their thumb.
USG Scan Of All Body Parts
Can help diagnose a variety of conditions and to assess organ damage following illness and to help physicians evaluate symptoms such as pain, swelling, infection, etc.
Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body’s internal organs, including but not limited to the:
Heart and blood vessels, including the abdominal aorta and its major branches, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries, intestines and unborn child (fetus) in pregnant patients, eyes, thyroid and parathyroid glands, salivary glands, scrotum (testicles), breast, brain in infants, hips in infants, spine in infants.
Ultrasound is also used to:
Guide procedures such as needle biopsies, in which needles are used to sample cells from an abnormal area for laboratory testing. Image the breasts and guide biopsy of breast cancer. Diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including valve problems and congestive heart failure, and assess damage after a heart attack.
